AHCC®Study Results
Infectious Disease
RESEARCHEradication of persistent human papillomavirus infections
AHCC® may increase the clearance rate of HPV infection by supporting the immune system
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is the virus that causes cervical cancer, and about 80% of women get infected with it at least once in their lifetime. In most cases, the virus is eliminated spontaneously by the immune system, but it can cause cancer if the viral infection chronically persists over several years. Although HPV vaccine is available to prevent infection, there is currently no treatment for post-infection.
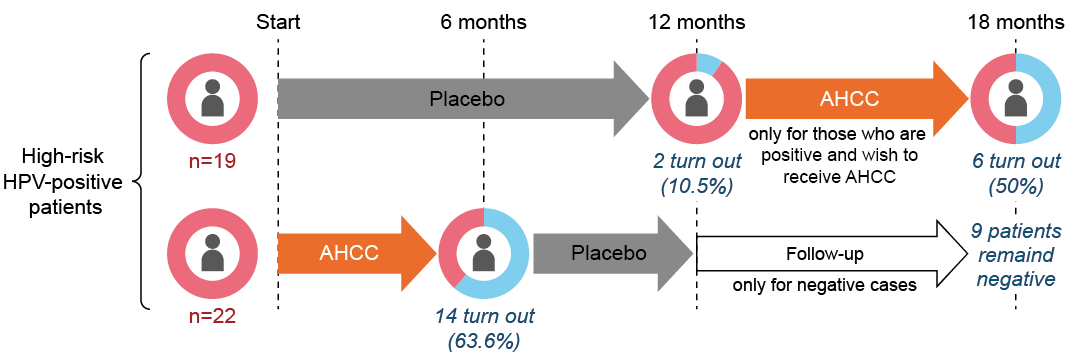
When women with persistent HPV infection for more than two years took AHCC®, 14 of 22 women became HPV negative after six months. In addition, AHCC® supplementation increased the number of T cells as well, which play a central role in the immune response.
These suggest that AHCC® supports the immune system and is expected to help eliminate HPV.
Judith A. Smith et al., Frontiers in Oncology, 12: 881902 (2022)
Clinical study
Design: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study
Subject: 41 patients persistently infected with high-risk HPV for at least 2 years
Groups: AHCC® + placebo for 6 months each (n=22) and placebo for 12 months (n=19)
Dose: AHCC® 3 g/day
Endpoints: Clearance of HPV infection, number of T cells
Result
After AHCC® intake for 6 months, about 60% of the patients infected with high-risk HPV showed resolution of the infection. AHCC® supplementation also increased T-cell counts, indicating that AHCC® may eliminate HPV by modulating immunity.
RESEARCHViral infection
AHCC® is expected to stimulate protective immune response against various viral infections.
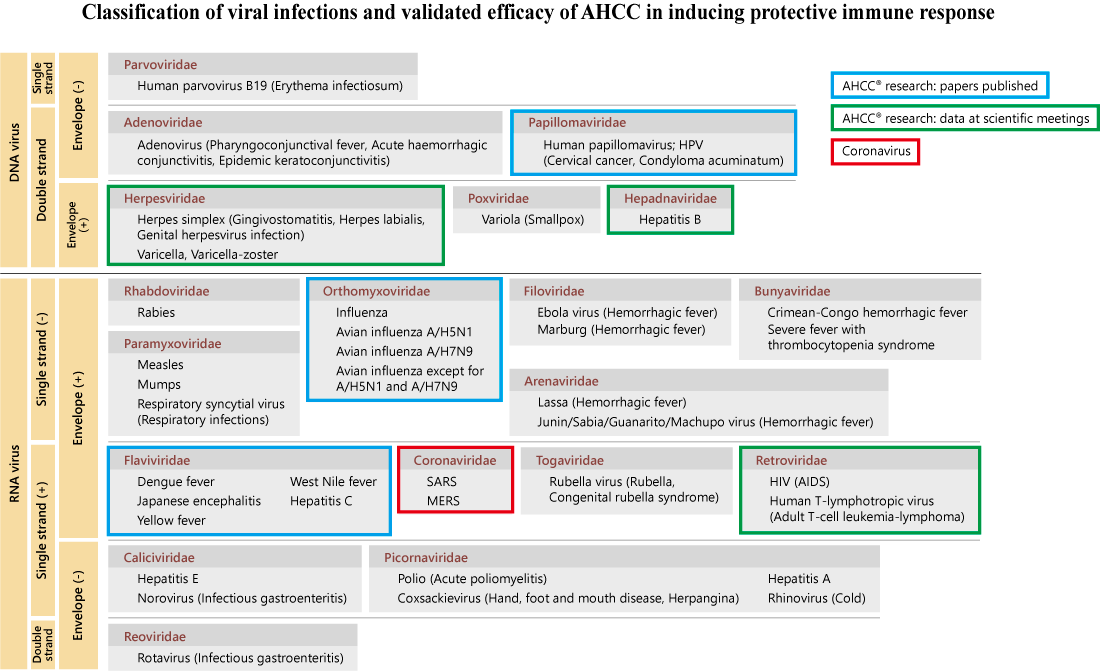
AHCC® has been studied about its efficacy for different types of bacterial and viral infectious diseases
including West Nile virus, influenza virus, hepatitis virus, and human papillomavirus (HPV).
In those studies, it is shown that NK (natural killer) cell, NK-T (natural killer T) cell, and γ δ T (gamma delta
T) cell, are modulated and activated by AHCC® intake, so the effect of AHCC® on infectious diseases is
considered to be an activation of host innate immunity which is responsible for an initial defense of the immune system.
In addition, such immunomodulatory effects of AHCC® are studied and reported in other types of diseases.
Therefore, although the efficacy of AHCC® against coronavirus has not been specifically evaluated, AHCC® is expected to be
effective in prevention and clearance of various infectious pathogens including coronavirus, by modulating and
optimizing host immune functions.
Francesco Di Pierro et al., Minerva Gastroenterol Dietol, 66(2): 172-176 (2020)
Review paper
Comprehensive evaluation on past studies regarding the immunomodulative effect and preventive effect of AHCC® against various viral infections suggested that AHCC® could prevent infection with human pathogenic coronaviruses including SARS-CoV-2 and increase in severity of the infection.
RESEARCHImmune cell activation by combining with a flu shot.
The number of immune cells and antibody titers were increased in healthy adults after flu shot.
AHCC® administration to healthy adults for 3 weeks starting from the day of infulenza vaccination increased the
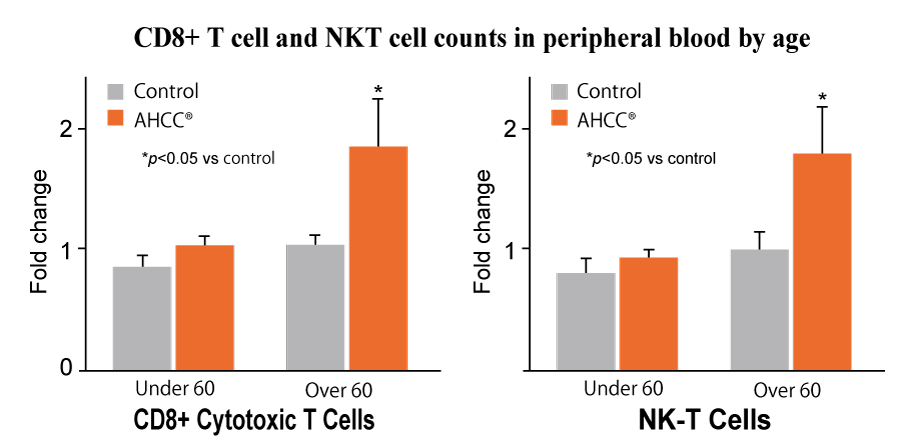
number of NK cells and cytotoxic T cells in the AHCC® group compared to the control group. In addition,
a significant rise in antibody titers (the amount and strength of antibodies) were observed in the AHCC® group.
These findings suggest that AHCC® intake could support the effect of influenza vaccination to prevent infection
and aggravation.
Brooke E Roman et al., Nutrition Research, 33(1): 12-17 (2013)
Clinical study
Design: A randomized, controlled trial
Subject: 29 healthy volunteers
Groups: Influenza vaccination + AHCC® (AHCC®: n=14) and influenza vaccination alone (control: n=15)
Dose and period: 3.0 g/day for 3 weeks from the day of vaccination
Endpoints: Comparison of lymphocyte populations measured by flow cytometry and levels of serum antibody
titers and plasma cytokines between day 0 and 3 weeks after
Results
The AHCC® group increased NK-T cells and CD8+ T cells compared to the control group. Furthermore, AHCC®
supplementation significantly improved the protective antibody titer level to influenza B, indicating that
AHCC® augments vaccine-associated effects.
Data are expressed as means±standard error of the mean (SEM).
RESEARCHOpportunistic infections associated with weakened immune system
AHCC® may support to prevent opportunistic infections and keep good health.
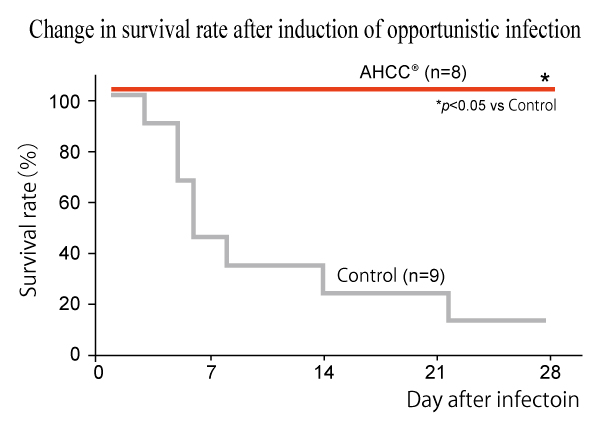
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), a pathogen that may cause fatal opportunistic infection, was inoculated to immunosuppressed mice. After 4 weeks of AHCC® administration, the survival duration was significantly extended compared to the control group. As AHCC® also showed significant extension of the survival duration with other similar studies with Candida albicans or Pseudomonas aeruginosa, AHCC® is expected to help maintain a good condition even under compromised immune system.
Hiroko Ishibashi et al., Yakugaku Zasshi, 120(8): 715-719 (2000)
Non-clinical study (in vivo)
Animal: 4-week-old male ICR/SPF mice immunosuppressed by cyclophosphamide treatment
Groups: AHCC® (n=8) and control (n=9)
Dose and period: 500 mg/kg/day for 4 weeks
Evaluation: Survival duration after inoculation of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
Results
It was revealed that AHCC® significantly prolonged survival time and alleviated severity of opportunistic infections.