AHCC®Study Results
Immunity
RESEARCHActivation of dendritic cells
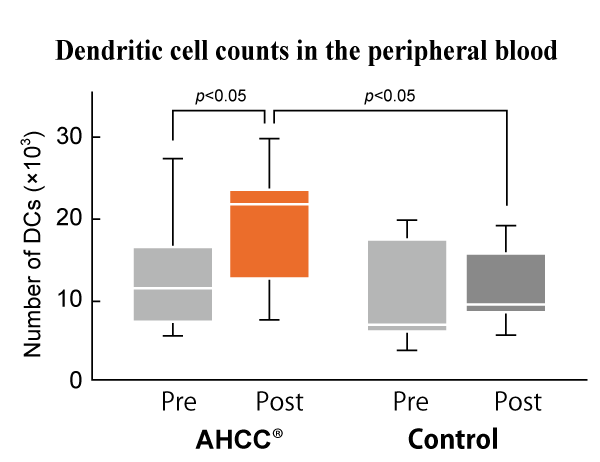
The number of dendritic cells, the commanders-in-chief of mucosal immune defenses, was increased in healthy adults.
The number of dendritic cells (DCs) was significantly increased by four weeks of AHCC® administration to healthy adults compare to the baseline and the placebo group.
DCs control immune response against infections as well as immune tolerance not to attack the body’s own cells.
It is suggested that AHCC® could help to maintain healthy immune functions by increasing DCs.
Naoyoshi Terakawa et al., Nutrition and Cancer, 60(5): 643-651 (2008)
Clinical study
Design: Double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
Subject: 21 healthy volunteers
Groups: AHCC® (n=10) and Control(placebo) (n=11)
Dose and period: 3 g/day for 4 weeks
Endpoint: Dendritic cells (DCs) count in peripheral blood mononuclear cells by flow cytometer
Results
AHCC® intake significantly increased the number of DCs, suggesting that AHCC® might contribute to sustention and modulation of immune functions.
Data are presented in a box-and-whisker plot (upper quartile: 75 percentile, median: 50 percentile, lower quartile: 25 percentile, upper whisker: 90 percentile, and lower whisker: 10 percentile).
RESEARCHImmune cell activation
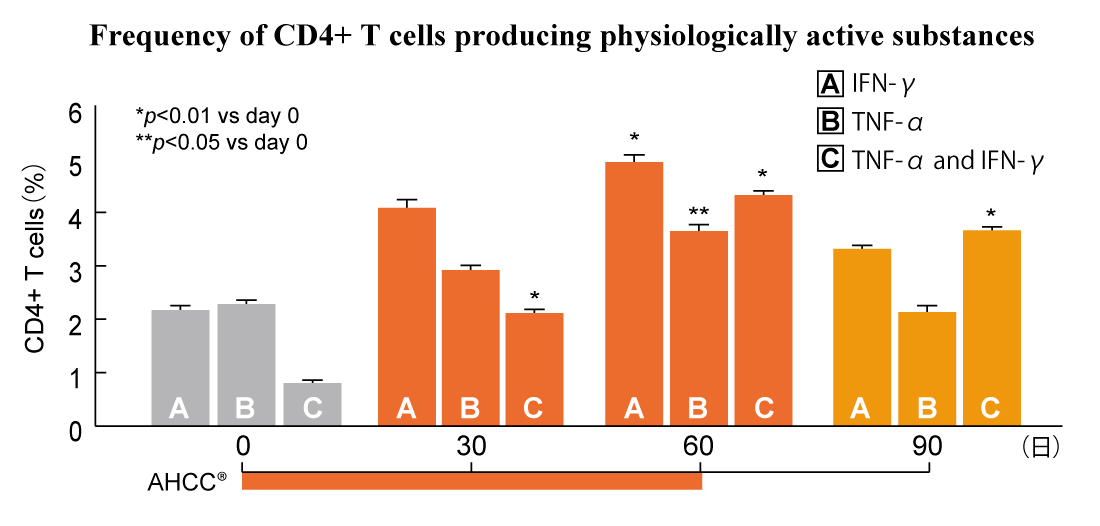
The levels of bioactive substances related to immune responses were increased in healthy adults, and kept high for 30 days after stopping intake.
Sixty days of AHCC® intake increased production of cytokines*1 (IFN-γ & TNF-α) by T cells*2 in 30 healthy volunteers over 50 years old. Additionally, the cytokine levels were kept higher than that of at the baseline even 30 days after stopping intake of AHCC®. These results suggest that AHCC® fortifies the immune response in healthy elderly people.
Zhinan Yin et al., Human Immunology, 71(12): 1187-1190 (2010)
Clinical study
Design: An open-label trial
Subject: 30 healthy volunteers over 50 years old
Dose and period: AHCC® 3 g/day for 60 days
Endpoints: IFN-γand TNF-α levels produced by CD4+ and CD8+ T cells
Results
AHCC® intake significantly increased the frequency of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells producing IFN-γalone, TNF-α alone, or both cytokines. In addition, the frequency of such cells remained high even 30 days after discontinuing the intake of AHCC®. These findings suggest that AHCC® could enhance CD4+ and CD8+ T cell immune responses.
*1:Cytokines: Bioactive substances consist of small secreted proteins released by mainly immune cells with a specific effect on the interactions and communications between cells.
*2:T cell(s): A type of lymphocyte that plays a central role in the adaptive immune response.